-
材小蠹族(Xyleborini)昆虫又称食菌小蠹,是一类蛀干害虫同时具有经济意义,隶属于鞘翅目(Coleoptera),象虫科(Curculionidae),小蠹亚科(Scolytinae)[1-2]。目前该族包括37属,约1 200种[2-3],中国记载10属42种[4]。材小蠹族类群主要取食木质部中的真菌,堵塞疏导组织,并且自身也携带真菌甚至携带病原体入侵植物并加速植物死亡[5]。Xyleborus glabratus Eichhoff所携带的病原菌,就曾在美国的东南部造成了鳄梨(Persea americana Mill. )的大面积死亡,并且在北美洲该族已经成为最具侵略性和攻击性的小蠹类蛀干害虫[3,6]。
小粒绒盾小蠹(Xyleborinus saxesenii(Ratzeburg,1873)),隶属于材小蠹族(Xyleborini),绒盾小蠹属(Xyleborinus)。殷蕙芬[7]1984年将材小蠹族的32种归在材小蠹属下,1991年材小蠹族分成10个属[8],1837年,小粒绒盾小蠹由Ratzeburg发现并定名为Bostrichus saxesenii[9-11],该种有21个同物异名[12-14],多数学者将其称为小粒材小蠹(Xyleborus saxeseni)[15-16],但此命名法未将材小蠹族分属,本文根据形态学观察和测序结果,将该材小蠹分到绒盾小蠹属下,为小粒绒盾小蠹。
小粒绒盾小蠹主要分布在中国(江西、云南、安徽、浙江、广西、福建、贵州、湖南、吉林、江苏、新疆、西藏、台湾、山西、陕西、四川),朝鲜,日本,越南,加拿大,北美,南美,阿根廷,巴西,智利,厄瓜多尔,巴拉圭,乌拉圭等[11,17-18],已知寄主包括橡胶树(Hevea brasiliensis,(H.B.K)Mull. Arg.),五倍子树( Rhus chinensis ,Mill.),山核桃(Carya cathayensis,Sarg.),苹果(Malus pumila,Mill.),云杉(Picea asperata,Mast.),栎树(Quercus stenophylla,Makino),杨梅(Myrica rubra,(Lour.)S. et Zucc.),柿子(Diospyros kaki,Thunb.),锥栗(Castanea henryi,(Skan)Rehd. et Wils. ),桉属植物(Eucalyptus sp.,L'Hér.),槭属植物(Acer sp.,L.),松属植物( Pinus sp. ,Linn),等[14,16,18-21]。
2022年3月,在崂山地区设置多层漏斗型小蠹诱捕器,悬挂地的林分主要是黑松林,周围也有刺槐等阔叶树。在对崂山区小蠹种类监测过程中,发现小蠹诱捕器内收集到一种小蠹,经形态学和分子生物学鉴定。旨在为小蠹类蛀干害虫快速DNA鉴定以及溯源分析提供基础数据。
-
2022年3月,在山东省青岛市崂山区(36.315929° N,120.603775° E)设置小蠹诱捕器诱集昆虫成虫。
-
采集到的样本储存于无水乙醇中,使用超景深显微镜(基恩士Kenyence VHX-7000)对小蠹的成虫形态特征进行观察和拍照。
-
随机抽取4头小蠹成虫,挑胸部和腹部组织,采用T5 Direct PCR Kit(Animal Tissue)试剂盒,提取个体基因组DNA,置于−20 ℃保存待用。
利用小蠹亚科通用引物S1718和A2411 [22]扩增COⅠ 基因,PCR扩增体系为2 × T5 Direct PCR Kit(Animal Tissue)13 μL,S1718 1 μL,A2411 1 μL,DNA模板2 μL和ddH2O 8 μL共25 μL。PCR反应程序为94 ℃预变性3 min;94 ℃变性45 s,47.2 ℃退火1 min,72 ℃延伸1 min,共进行35次循环;72 ℃延伸10 min;产物置于4 ℃保存。PCR扩增产物送北京擎科生物科技有限公司进行测序。
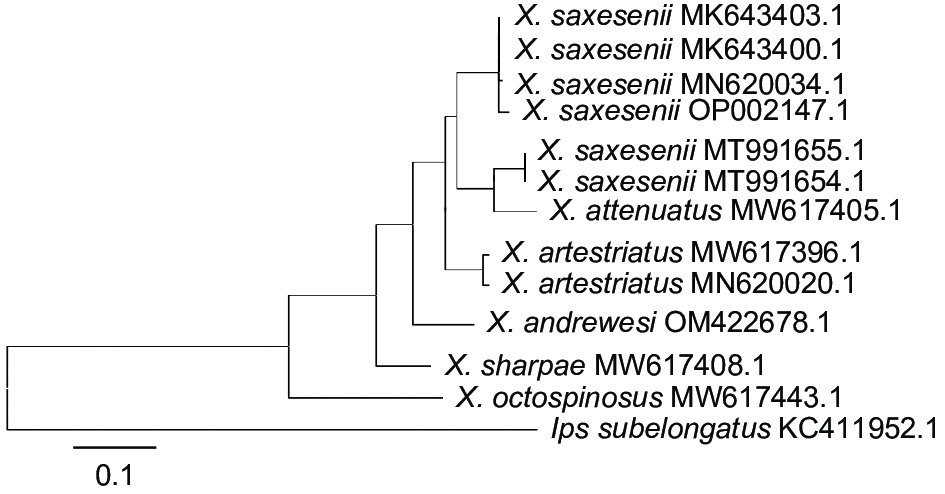
以COⅠ 基因序列建树:选取本试验的X. saxesenii序列(Genbank No. OP002147.1),来自Genbank的12条序列作为参考序列(表1),落叶松八齿小蠹(Ips subelongatus Motschulsky)(Genbank No. KC411952.1)作为外群,运用MAGA 7[23]最大似然法(ML)构建系统发育树[24-26]。
Genbank登录号
Genbank accession No.物种名称
Species采集地
LocationOP002147.1 小粒绒盾小蠹 X. saxesenii 中国,青岛 China: Qingdao MK643403.1 小粒绒盾小蠹 X. saxesenii 美国,科罗拉多州 USA: Colorado MK643400.1 小粒绒盾小蠹 X. saxesenii 美国,科罗拉多州 USA: Colorado MT991655.1 小粒绒盾小蠹 X. saxesenii 美国 USA MN620034.1 小粒绒盾小蠹 X. saxesenii 东南亚 Southeast Asian MT991654.1 小粒绒盾小蠹 X. saxesenii 美国 USA MW617396.1 纹盾材小蠹 Xyleborinus artestriatus Eichhoff 中国 China MN620020.1 纹盾材小蠹 Xyleborinus artestriatus Eichhoff 东南亚 Southeast Asian MW617443.1 Xyleborinus actospinosus Schaufuss 马达加斯加 Madagascar MW617408.1 Xyleborinus sharpae Hopkins, 马达加斯加 Madagascar MW617405.1 Xyleborinus attenuatus Blandford, 马达加斯加 Madagascar OM422678.1 Xyleborinus andrewesi Blandford, 马达加斯加 Madagascar KC411952.1 落叶松八齿小蠹 Ips subelongatus Motschulsky 中国 China Table 1. Sequence information in tree construction of Scolytinae
-
小粒绒盾小蠹体长2.0 mm,圆柱形,黑褐色,鞘翅后部及斜面颜色稍浅,红褐色,触角和足黄褐色(a、b)。复眼类似肾形,前缘中部具深的缺刻(c);触角锤状部端部有如经过切削而成的圆形削面,其上具圆形毛缝(d);前胸背板背面观后方前圆,成长盾形(e)。鞘翅基部翅缝处下陷成坑,三角形,内生浓密绒毛,小盾片从中成锥状突起,易被绒毛遮盖(e);鞘翅侧面观鞘翅背缘前部2/3平直延伸,后部的1/3弓曲下降(b);鞘翅自斜面前缘开始,沟间部具突起的颗瘤,由前向后略许增大,成为纵列,第2沟间部无颗瘤(f)。如(图1)。
-
采集于青岛市崂山区诱捕器内的4头小蠹成虫样本,通过分子鉴定均属于同一物种;该小蠹COⅠ 基因长度为698 bp(OP002147.1),经Blast对比可知,该小蠹与美国序列样本(MK643403.1、MK643400.1)和东南亚序列样本(MN620034.1)相似度达99%。ML系统发育树(图2)显示该小蠹(OP002147.1)与X. saxesenii聚为一支,但与同属不同种的纹盾材小蠹(X. artestriatus)(Eichhoff,1878)(MW617396.1、MN620020.1)、X. octospinosus(MW617443.1)、X. sharpae(MW617408.1)、X. attenuatus(MW617405.1)、X. andrewesi(OM422678.1)分在不同支上。
-
材小蠹族是重要的林业害虫,主要分布在热带和温带地区[11],寄主广泛,包括针叶树和阔叶树,几乎终生生活在树木木质部中,难以被发觉。大多数种类蛀食衰弱树、倒木、濒死树木或死树[27]。据刘章华等人[21]报道小粒绒盾小蠹在浙江地区为害锥栗,1年发生3~5代,以成虫越冬,全年均可见到成虫。本研究中诱捕器监测到的小粒绒盾小蠹主要出现在4—6月,推测由于寄主、环境和地理因素因,该虫在崂山区的为害情况与浙江地区不同,且该虫只在诱捕器内发现,因此其寄主种类和生活史还有待研究。
本文并未对小粒绒盾小蠹雄虫进行描述,因为材小蠹族所有雄虫为单倍体[28],相比雌虫体型短小,样貌丑陋无翅且数量少,通常不用来鉴定和描述使用[29],在诱集过程中也未发现雄虫。
Cognato利用COⅠ 基因研究了Conophthorus sp.的系统发生和地理环境与寄主对该属昆虫的影响[30];常虹等区分了齿小蠹属Ips sp.的不同物种[31];王银竹等研究了长小蠹科Platypodidae昆虫的系统发育关系[32]。本研究在诱集过程中发现,诱集到的小粒绒盾小蠹在形态学上与同属的小蠹难以区分,或是因为肢体残缺而无法辨别,因此利用COⅠ 基因序列比对进行小粒绒盾小蠹分子鉴定可以有效弥补形态鉴定的不足。
材小蠹族类群被称为食菌小蠹,通过以真菌覆盖的木材为食[18],并可传播真菌或病原菌[11]。据文献记载,1844年Hartig鉴定北方毛胸小蠹 (Anisandrus dispar,F.)体内存在的共生菌为白落丛梗孢-Monilia candida,到1967年,Batra[33]鉴定该共生真菌为哈氏虫道真菌(Ambrosiella hartigii,L.R. Batra),王天龙[34]鉴定培养出3种足距小蠹属(Xylosandrus sp.)储菌器的共生真菌,短翅足距小蠹(Xylosandrus brevis Eichhoff)、X. germanus Blandford的共生真菌均为哈氏虫道真菌,黑色枝小蠹(Xylosandrus compactus Eichhoff)的共生真菌为Ambrosiella xylebori Brader ex Arx & Hennebert。小粒绒盾小蠹共生真菌种类及联合作用方式有待进一步研究。
-
本文作者针对一种小蠹进行研究,经形态学和分子生物学鉴定,明确该诱集到的小蠹为小粒绒盾小蠹,为山东首次报道,研究结果丰富了生物多样性。该小蠹最主要的形态特征为鞘翅自斜面前缘开始,沟间部具突起的颗瘤,由前向后略许增大,成为纵列,第2沟间部无颗瘤,该特征可作为小粒绒盾小蠹的鉴别特征。
Morphology and Molecular Identification of Xyleborinus saxesenii(Ratzeburg,1873)(Coleoptera: Scolytinae)
- Received Date: 2022-12-02
- Accepted Date: 2023-01-13
- Available Online: 2023-06-20
Abstract:







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: