-
G蛋白是一类GTP结合蛋白, 按照G蛋白分子量和亚基组成可分为异源三聚体G蛋白、小G蛋白和几种特殊的GTP结合蛋白[1]。小G蛋白家族又称为Ras超家族, 根据其成员之间结构和功能的相似性, 将Ras超家族分为五个不同的家族, 分别是Ras、Rab、Arf、Ran和Rho家族[2], 其中Rho家族又可被分为CDC42、RAC和RHO三个亚家族[3-4]。这五个家族成员在细胞中参与了不同的生物学过程, 例如Ras家族成员参与调控细胞增殖, Rab家族和Arf家族成员在介导不同膜细胞器之间的囊泡运输中发挥重要作用, Ran家族成员主要调控与细胞核相关的一些细胞活动, 而Rho家族成员在细胞骨架重组及信号转导中行使重要功能[5]。
与动物或真菌Ras超家族不同, 植物没有Ras家族, 而植物中Rho形成了独特的一类, 称为ROP(Rho-related proteins from plants)[5]。自1993年首次从豌豆中发现Rho相似性GTPase以来, 已在拟南芥、水稻与玉米等多种植物中进行了鉴定[6]。ROP主要在与GTP结合的活性形式和与GDP结合的非活性形式之间循环, 该循环过程需要多种蛋白的参与, 如鸟苷酸交换因子(guanine nucleotide exchange factor, GEF)、GTPase激活蛋白(GTPase activating protein, GAP)、鸟苷酸解离抑制因子(GDP dissociation inhibitor, GDI)等。一旦受体感知到上游信号, 鸟苷酸交换因子就催化ROP从GDP结合的非活性形式转换为GTP结合的活性形式, 具有活性的ROP蛋白与下游效应蛋白结合发挥其生理功能[7]。ROP蛋白的结构极为保守, 主要包含与鸟苷酸结合和水解有关的5个高度保守结构域、1个效应因子结合区、1个插入序列和C端高度可变区。GTP结合结构域和效应因子结合区决定ROP蛋白的功能, 插入序列的功能目前尚不清楚, C端高度可变区决定ROP蛋白的亚细胞定位[8]。
ROP在植物发育与抗逆等生物学过程中具有重要的功能。在叶表皮铺板细胞中, 拟南芥ROP2调节PIN1的内吞过程[9]。在拟南芥胚胎发育阶段, ROP3在维持PIN1和PIN3在细胞膜上的极性分布方面具有重要作用[10]。拟南芥中多种ROP基因在花粉管尖端表达, 其中ROP1对花粉管的极性生长起主要作用[11]。ROP还参与根毛的发育, 超表达拟南芥ROP2, 能增加根毛数量和密度, 而AtROP4控制根毛的发生和尖端的伸长[12]。此外, 拟南芥保卫细胞中的ROP2能够被光激活来抑制光诱导的气孔张开[13]。目前, 在拟南芥基因组中共发现了10个ROP基因成员, 水稻和玉米分别发现7个和9个[6]。虽然一些研究都表明ROPs广泛参与了植物对激素, 环境等信号的响应及植物生长发育过程, 但各个ROP成员的功能还有待进一步解析。杨树全基因组序列虽已公布, 但对ROP基因家族成员尚未进行系统分析[14]。
本研究利用拟南芥ROP氨基酸序列, 在杨树基因组数据库中进行同源比对, 共鉴定出13个PtROP基因序列。在此基础上, 对杨树PtROP基因进行了系统进化、基因结构及保守结构域分析, 并对其在不同组织和不同胁迫条件下的表达情况进行了分析, 构建了其基因调控网络。研究结果为将来系统解析杨树ROP基因的功能奠定了基础。
HTML
-
实验所用银腺杨(P. alba×P. glandulosa)无性系84K, 由中国林业科学研究院林木遗传育种国家重点实验室保存。杨树幼苗培养于人工培养箱, 培养条件为16 h光照/8 h黑暗, 昼夜温度为23℃/20℃。分别取杨树幼株(株高约80 cm)的顶端、幼叶、成熟叶、茎顶端、茎下部及根, 分别提取总RNA。
-
总RNA提取参见QIAGEN RNeasy Plant Kit RNA描述的方法进行。
-
用带有Oligo(dT)的磁珠富集样品总RNA中的mRNA, 将富集的mRNA片段化后用随机引物合成第一链cDNA, 随后合成双链cDNA, 再对双链cDNA进行纯化, 末端修复和添加测序接头, 最后进行PCR扩增, 建好的测序文库用Illumina HiSeqTM 2000测序平台进行pair-end 100 bp测序, 每个样品分别获得2G clean data。测序原始数据去除接头及低质量reads, 获得的clean reads利用TopHat2比对到毛果杨基因组上(http://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/pz/portal.html#!info?alias=Org_Ptrichocarpa, release 3.0)。标准化的FPKM值反映基因的表达水平。
-
拟南芥ROP基因及其编码的蛋白质序列来源于TAIR(http://www.arabidopsis.org/index.jsp)数据库。以拟南芥ROP蛋白序列为搜索对象, 通过blastp程序在毛果杨基因组数据库(http://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/pz/portal.html#!info?alias=Org_Ptrichocarpa, release 3.0)中搜索相似的蛋白序列, 选取E≤10-10的序列作为候选序列, 获得的毛果杨ROP基因命名为PtROP1-13。
-
将拟南芥和杨树PtROP氨基酸序列保存为FASTA格式, 用Clustal X[15]对其氨基酸序列进行多序列比对, 分别利用MEGA5.0[16]中Maximum-Likelihood(ML)法和Neighbor-Joining(NJ)法构建系统进化树。
-
运用在杨树基因组数据库中下载的基因组DNA序列及CDS序列使用GSDS[17]程序(http://gsds.cbi.pku.edu.cn/)对杨树PtROP基因的外显子和内含子进行分析。杨树PtROP基因组DNA序列及CDS序列下载自Phytozome数据库(http://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/pz/portal.html#!info?alias=Org_Ptrichocarpa, release 3.0)。
-
分析杨树不同胁迫条件下的PtROP基因成员的表达模式所用的基因芯片数据来自NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus(GEO)[18]数据库。
-
利用网站(http://10.13.200.25/PoplarGene/index.php)对杨树ROP基因进行功能网络分析。
1.1. 实验材料
1.2. 总RNA的提取
1.3. 转录组测序
1.4. 数据来源
1.5. 系统进化树分析
1.6. 基因结构分析
1.7. 基因表达分析
1.8. 杨树PtROP基因功能网络分析
-
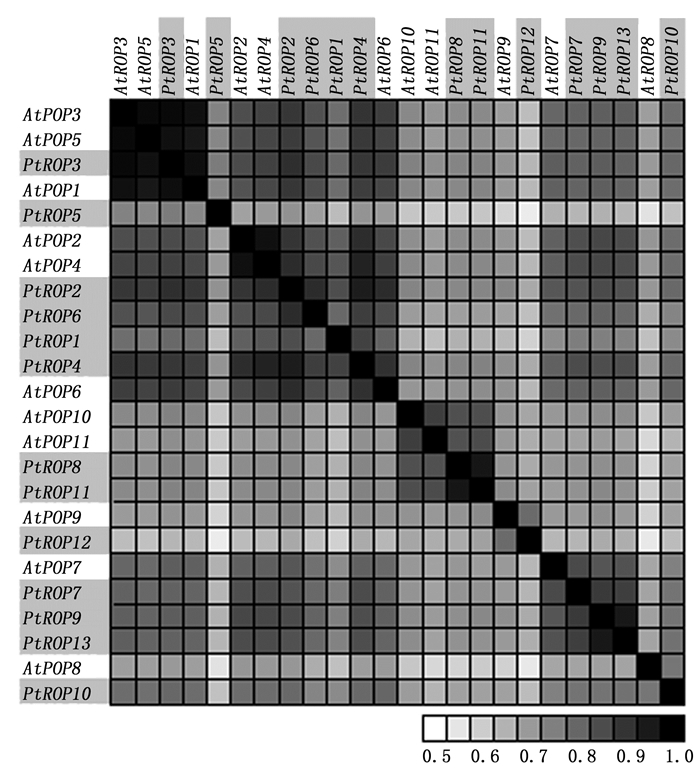
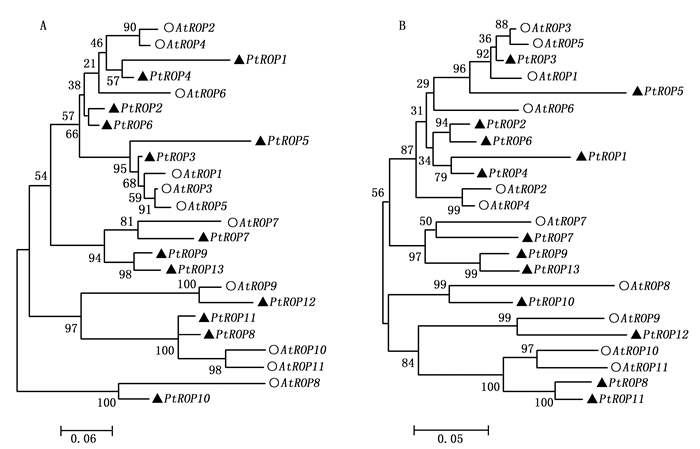
利用拟南芥ROP氨基酸序列, 在杨树全基因组数据库中搜索相似的氨基酸序列, 以E≤10-10作为候选标准, 共得到13个PtROP基因家族成员(表 1)。13个PtROP基因长度在2 047~6 862 bp之间, 但其蛋白序列约为200个氨基酸左右, 蛋白质分子量约22 kDa, 等电点约为9, 其中毛果杨基因组数据获取的PtROP10基因序列不完整。利用两种不同的算法, 即最大似然法(ML)和邻接法(NJ), 对杨树和拟南芥ROP蛋白进行系统进化分析, 发现用两种算法得到的杨树及拟南芥ROP蛋白进化关系相似(图 1)。根据ROP家族成员在杨树染色体上的分布顺序, 将其命名为PtROP1-13。Zheng和Yang等根据氨基酸序列相似性及C端高度可变区结构, 将拟南芥ROP蛋白分为四类, 即AtROP8、AtROP9-11、AtROP7和AtROP1-6[19]。对杨树及拟南芥ROP蛋白系统进化关系分析显示, 同拟南芥ROP蛋白一样, 这四类中均有相应的杨树ROP蛋白, 分别对应为: 第一类(PtROP10)、第二类(PtROP8、PtROP11、PtROP12)、第三类(PtROP7、PtROP9、PtROP13)及第四类(PtROP1-6)。与拟南芥相比, 杨树在第三类增加了两个ROP基因成员。
杨树基因gene 基因号gene number 基因在染色体上的位置location 基因长度length of gene/bp 蛋白质长度length of protain/aa 等电点pI/(分子量/kDa) PtROP1 Potri.002G019500 Chr02(-)1130440-1133737 3 298 202 9.49/22.305 64 PtROP2 Potri.004G174900 Chr04(+)19344459-19348452 3 994 198 9.33/21.859 42 PtROP3 Potri.005G110700 Chr05(-)8522678-8526079 3 402 197 9.32/21.570 95 PtROP4 Potri.005G242000 Chr05(+)24796222-24799414 3 193 197 9.28/21.692 14 PtROP5 Potri.007G061500 Chr07(+)6811340-6814779 3 440 228 8.18/25.038 61 PtROP6 Potri.009G134600 Chr09(+)10876427-10880720 4 294 210 9.50/23.298 15 PtROP7 Potri.011G061500 Chr11(-)5482983-5485029 2 047 196 9.30/21.845 30 PtROP8 Potri.012G077800 Chr12(-)10352323-10359184 6 862 211 9.35/23.448 24 PtROP9 Potri.013G123800 Chr13(-)13754749-13757500 2 752 197 9.45/21.861 31 PtROP10 Potri.014G051800 Chr14(-)4107009-4109732 2 724 191 9.07/21.389 68 PtROP11 Potri.015G073000 Chr15(-)9749868-9756148 6 281 211 9.21/23.465 25 PtROP12 Potri.018G083400 Chr18(-)11015972-11018214 2 243 226 9.37/25.242 44 PtROP13 Potri.019G092300 Chr19(+)12299464-12301826 2 363 197 9.53/21.797 27 Table 1. Basic information of Populus PtROP gene
-
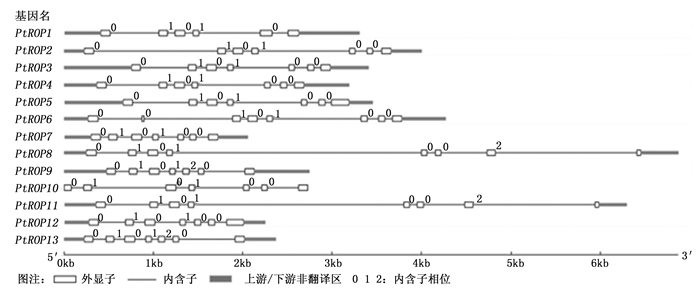
通过对杨树PtROP基因结构(外显子/内含子)分析显示, 杨树13个PtROP基因成员结构相似性很高, 外显子数目为6~8个。其中, 9个PtROP基因成员(PtROP2、PtROP3、PtROP4、PtROP5、PtROP7、PtROP9、PtROP10、PtROP12与PtROP13)存在7个外显子, 3个PtROP基因(PtROP6、PtROP8及PtROP11)有8个外显子, 1个PtROP基因(PtROP1)具有6个外显子(图 2)。对杨树及拟南芥ROP氨基酸序列相似性比较, 发现杨树与拟南芥ROP氨基酸序列在相对应的分类中相似性很高(图 3), 可能为直系同源关系。而杨树中有四对ROP(PtROP1/PtROP4、PtROP2/PtROP6、PtROP8/PtROP11、PtROP9/PtROP13)氨基酸序列一致性很高(图 3), 说明他们是旁系同源关系, 可能来自染色体加倍或基因的复制。
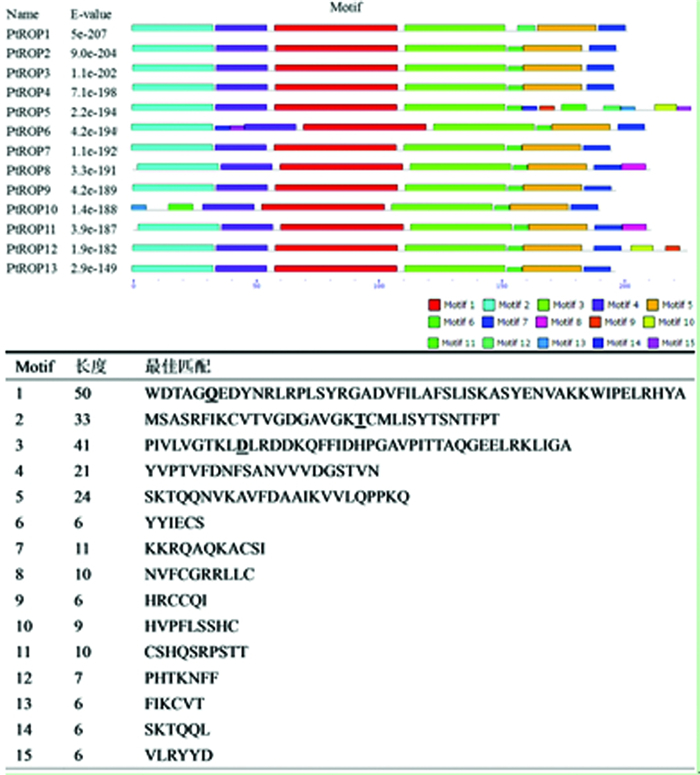
利用MEME结构域搜索工具在杨树PtROP中检测到15个保守的结构域。结果表明, PtROP10中不存在motif 2, PtROP5不具有motif 5, 而其它ROP均具有motif 1-7。Motif 1、2、3及5代表了ROP蛋白与GTP结合的结构域(图 4), 这四个结构域中都存在与GTP结合的保守结合位点。PtROP5虽然不具有motif 5, 但它具有其它与GTP结合的保守结合位点。对杨树PtROP蛋白motif 2中第20位的苏氨酸、motif 3中第10位的天冬氨酸分别进行点突变, 能够改变ROP蛋白与GTP的亲和性, 使其成为显性失活形式。如果对杨树PtROP蛋白motif 1中将第6位的谷氨酰胺突变为亮氨酸, ROP蛋白就成为了持续活性型形式(图 4)。
-
通过比较其系统进化关系、基因结构及氨基酸序列相似性, 在杨树PtROP基因家族中共鉴定得到4对旁系同源基因对, 分别是PtROP1/PtROP4、PtROP2/PtROP6、PtROP8/PtROP11及PtROP9/PtROP13, 这些基因对之间在氨基酸序列、内含子的插入大小及插入位点都极为保守。PtROP1/PtOP4、PtROP2/PtROP6、PtROP8/PtROP11、PtROP9/PtROP13所在染色体片段区域的大部分基因都是同源基因, 因此这四个基因对可能是由于染色体复制产生的(图 5)。计算这四个基因对非同义替换率和同义替换率的比值, 发现它们都小于0.4, 因此基因对中的两个旁系同源基因复制后经历了纯化选择在功能上产生了一定程度的差异(表 2)。根据杨树扩张度λ=9.1×10-9, 估算出PtROP旁系同源基因对可能是在8.74到17.30百万年前产生的, 其中PtROP1/PtROP4产生的最早, 约在17.30百万年前; PtROP8/PtROP11产生的最晚, 约在8.74百万年前。而PtROP2/PtROP6、PtROP9/PtROP13分别是在13.98百万年前和11.77百万年前产生的, 这个时期与杨树最近一次在13百万年前发生的大规模片段复制时间大致相符[14]。
基因1 基因2 非同义替换率 同义替换率 非同义替换率/同义替换率 时期(百万年前) PtROP1 PtROP4 0.074 0.315 0.236 17.30 PtROP2 PtROP6 0.013 0.255 0.052 13.98 PtROP8 PtROP11 0.020 0.159 0.125 8.74 PtROP9 PtROP13 0.020 0.214 0.094 11.77 Table 2. Divergence between paralogous PtROP gene pairs
-
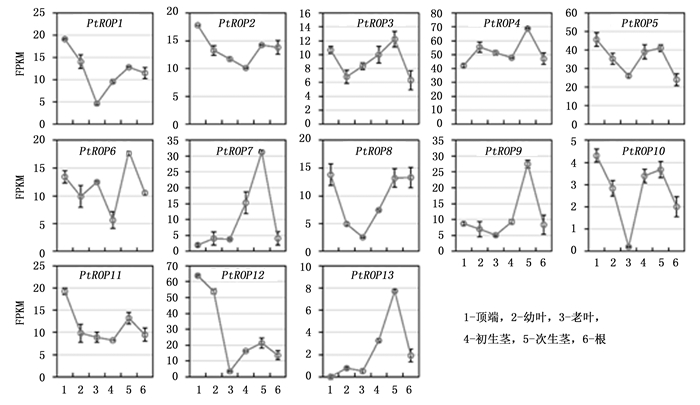
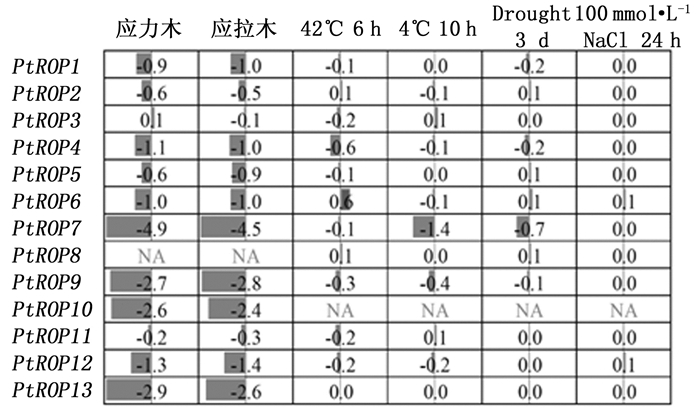
为了探究杨树PtROP基因可能参与的生物学过程, 利用课题组的RNA-seq数据和已公布的杨树基因芯片数据, 分析了杨树PtROP基因在不同组织及不同胁迫条件下的表达模式。与幼叶、老叶、幼茎、木质化茎及根相比, 杨树PtROP1、PtROP2、PtROP8、PtROP11及PtROP12在顶点的表达水平较高, 表明它们可能参与了顶端发育过程。PtROP7、PtROP9及ROP13特异性地在已木质化的茎中表达, 说明这些基因可能参与杨树次生生长。PtROP1、PtROP8、PtROP9及PtROP12在老叶中的表达量最低, 表明它们可能不参与光合作用及次生物质的代谢过程(图 6)。
在应拉木和应力木中PtROP7、PtROP9、PtROP10及PtROP13表达都显著下调, 且PtROP7、PtROP9及PtROP13在次生茎中特异性高表达, 表明这三个基因的表达受外力的调控。对高温、低温、干旱和盐胁迫条件下PtROP基因的表达分析发现, 13个基因中仅有PtROP7在低温条件下下调表达, 表明大部分PtROP基因可能不直接对高、低温、干旱和盐等胁迫响应, 或者其在胁迫条件下的稳定表达对细胞功能的维持具有重要作用(图 7)。
-
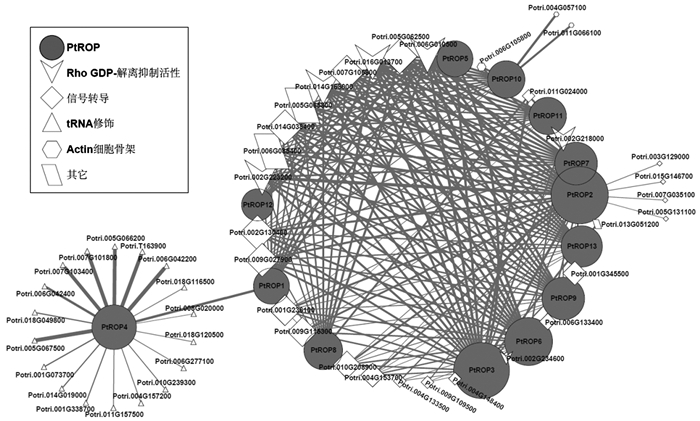
为了进一步解析PtROP基因的生物学功能, 构建了PtROP的功能基因网络。发现与PtROP基因紧密联系的基因主要分为四类, 即Rho GDP-解离抑制活性、信号转导、tRNA修饰及Actin细胞骨架(表 3)。其中, 在整个网络中大约50%的基因与信号转导相关, 并且这些基因与杨树PtROP基因的相关性都比较大, 这与拟南芥中ROP参与了信号转导的结果相符合, 说明PtROP基因具有功能保守性。13个基因中, 与PtROP2和PtROP3相关联的基因最多, 表明二者在整个调控网络中发挥主要作用。在网络中, 与tRNA修饰相关的基因占50%以上, 但仅有PtROP4与之相关联, 并且它们之间的相关性较小, 可能PtROP4广泛地参与到tRNA修饰中, 但不在其中起主要作用, 另外, PtROP4基因在13个PtROP基因中仅与PtROP1存在关联, 显示杨树PtROP4可能在进化过程中出现了功能分化(图 8)。
分类 基因号
gene number功能注释
tunction分类 基因号
gene number功能注释
functiontRNA修饰 Potri.001G073700 S-腺苷-L-甲硫氨酸依赖性甲基转移酶 信号转导 Potri.001G236100 Ras相关小G蛋白 tRNA Potri.001G338700 S-腺苷-L-甲硫氨酸依赖性甲基转移酶 signal Potri.004G148400 WD40重复蛋白 modification Potri.004G157200 核糖体蛋白S25家族蛋白 transduction Potri.004G153700 GTP结合蛋白 Potri.005G066200 S-腺苷-L-甲硫氨酸依赖性甲基转移酶 Potri.005G131100 WD40重复蛋白 Potri.005G067500 S-腺苷-L-甲硫氨酸依赖性甲基转移酶 Potri.006G133400 GTP激活蛋白 Potri.006G042200 S-腺苷-L-甲硫氨酸依赖性甲基转移酶 Potri.007G035100 WD40重复蛋白 Potri.006G042400 S-腺苷-L-甲硫氨酸依赖性甲基转移酶 Potri.009G027900 Ras相关小G蛋白 Potri.006G277100 tRNA甲基转移酶 Potri.009G109500 WD40重复蛋白 Potri.007G101800 S-腺苷-L-甲硫氨酸依赖性甲基转移酶 Potri.009G115300 GTP结合蛋白 Potri.007G103400 S-腺苷-L-甲硫氨酸依赖性甲基转移酶 Potri.010G208900 RabA Potri.008G020000 核糖体蛋白S25家族蛋白 Potri.011G024000 鸟苷酸交换因子 Potri.010G239300 核糖体蛋白S25家族蛋白 Potri.014G038400 WD40重复蛋白 Potri.011G157500 甲基转移酶 Potri.002G130400 WD40重复蛋白 Potri.014G019000 锚蛋白重复序列蛋白家族 actin细胞骨架 Potri.004G057100 SCAR蛋白 Potri.018G049800 S-腺苷-L-甲硫氨酸依赖性甲基转移酶 actin cytoskeleton Potri.006G105800 SCAR蛋白 Potri.018G116500 S-腺苷-L-甲硫氨酸依赖性甲基转移酶 Potri.011G066100 SCAR蛋白 Potri.018G120500 S-腺苷-L-甲硫氨酸依赖性甲基转移酶 其他 Potri.006G085400 生物素合成相关 Potri.T163900 S-腺苷-L-甲硫氨酸依赖性甲基转移酶 others Potri.005G065800 DNA结合相关 Potri.013G051200 转录激活因子 Table 3. Genes information in the PtROP gene functional network
2.1. 杨树PtROP基因鉴定及系统进化分析
2.2. PtROP基因结构及保守结构域分析
2.3. PtROP基因旁系同源基因对的复制
2.4. 在不同组织、不同胁迫条件下的表达
2.5. 杨树PtROP基因功能基因网络分析
-
杨树是全球广泛分布的重要经济树种, 具有生长迅速, 生物量大、轮伐期短等特点, 随着杨树全基因组测序的完成, 杨树已成为研究多年生林木生长发育的模式树木。在不同物种中对ROP基因的研究发现ROP基因广泛地参与了植物的生长发育和抗逆过程, 而且ROP基因在初生细胞壁和次生细胞壁的沉积过程中具有重要作用[20]。因此对于杨树ROP基因的研究, 不仅在揭示木本植物发育和抗逆机理上具有重要意义, 而且具有重要的应用价值。
本研究利用已知的拟南芥ROP氨基酸序列在杨树全基因组数据库中进行相似性序列搜索, 共检测到13个PtROP基因成员, 其中包含四个旁系同源基因对; 进化分析表明, 这些基因可能来自全基因组染色体复制。杨树PtROP基因结构分析、系统进化分析及氨基酸序列相似性分析表明, 杨树PtROP基因家族成员在结构与氨基酸序列上极为保守。杨树PtROP基因与拟南芥相同, 分为四类, 它们相对应的类别, 氨基酸序列相似度很高。对杨树PtROP的motif研究表明, 杨树和拟南芥ROP一样, 都具有相同的与GTP结合的保守结构域。这些研究结果预示着ROPs在杨树中具有类似的、保守的功能。
对杨树PtROP基因家族成员在不同组织、不同胁迫条件下的表达情况进行了分析, 发现不同的PtROP基因在不同的组织中表达存在差异, 表明它们可能参与了不同的生物学过程。研究发现拟南芥ROP11影响次生细胞壁的沉积, 在超表达持续活性型ROP11拟南芥中, 正在分化的木质部细胞次生壁上没有纹孔的形成, 而ROP效应因子ROPGEF4的缺失导致次生壁上纹孔数量减少[21]。桉树ROP1也能够影响次生细胞壁的沉积, 其在形成层和正在分化的木质部细胞中都有很高的表达水平, 在拟南芥中超表达持续活性型的桉树ROP1基因抑制次生木质部的木质化和木葡聚糖沉积[22]。本研究发现杨树PtROP7、PtROP9与PtROP13特异性地在茎的次生长生中高丰度表达, 表明这三个基因可能参与了杨树次生生长过程。PtROP7、PtROP9与PtROP13同属于杨树PtROP基因家族的第三类, 可能存在功能上的冗余, 以保障在茎的次生维管发育中发挥重要作用。
已有研究表明, 植物ROP蛋白参与了多种逆境胁迫。例如, 油菜ROP5和ROP9在高温胁迫后表达发生明显变化[23], 玉露桃冷害胁迫后, 果实中的ROP基因表达量显著降低[24]。本研究通过对高温、低温、干旱与盐等胁迫条件下杨树PtROP的表达分析发现, PtROP基因对这些胁迫没有产生显著响应, 可能是由于杨树PtROP基因功能的特化, 趋于基本维持细胞正常的信息与物质的流动。通过杨树PtROP的功能基因网络分析, 发现杨树PtROP基因主要参与了信号转导过程, 这与上述推测是一致的[25]。
-
本研究以杨树为模式, 在全基因组水平上对ROP基因的家族成员、基因结构、保守结构域、氨基酸序列相似性及表达模式进行了分析。发现杨树中共有13个PtROP基因, 它们的基因结构相似, 功能结构域是保守的。根据氨基酸序列相似性及C端高度可变区结构, 杨树PtROP被分为四类: 第一类(PtROP10)、第二类(PtROP8、PtROP11和PtROP12)、第三类(PtROP7、PtROP9和PtROP13)及第四类(PtROP1-6)。对PtROP基因的复制情况进行分析, 发现PtROP基因家族中存在四对旁系同源基因对(PtROP1/PtROP4、PtROP2/PtROP6、PtROP8/PtROP11及PtROP9/PtROP13), 它们都是通过全基因组复制产生的。四个基因对都经历了纯化选择。PtROP旁系同源基因对可能是在8.74到17.30百万年前产生的。对PtROP基因家族成员在不同组织和不同胁迫响应进行分析, 发现PtROP基因家族成员表达模式具有明显差异。通过构建PtROP功能基因网络, 发现PtROP可能参与了信号转导、tRNA修饰及细胞骨架形成等过程。
本研究系统分析了杨树PtROP家族的成员及其进化关系, 研究PtROP基因在木本植物发育过程中的表达特性和可能的功能, 为进一步研究其在木本植物特别是次生生长过程中的作用奠定了基础。













 DownLoad:
DownLoad: