-
MicroRNAs(miRNA)是一类由20~22个核苷酸构成的非编码小RNA,可通过结合靶基因mRNA的3′非翻译区(3′-untranslated region,3′-UTR)使其降解或者阻碍其转录,从而在转录后水平控制基因表达[1]。作为基因表达负调控子,miRNA主要在转录后水平调节植物基因表达[2],在植物新陈代谢、组织生长、器官发育分化以及细胞程序性凋亡中起重要作用[3-4]。此外,miRNA在植物感受逆境胁迫而做出适应性调整的过程中发挥着重要的作用。特别是在病原侵染过程中,miRNA能够调控植物抗病途径中的关键靶基因来决定病原与寄主的亲和关系(compatible/incompatible interaction)。
MYB(v-myb avian myeloblastosis viral oncogene homolog)是一类在其N端含有MYB结构域的转录因子(transcription factor,TF)[5]。MYB是植物中最大的一类转录因子家族,涉及水杨酸(salicylic acid,SA)、脱落酸(abscisic acid,ABA)及茉莉酸(jasmonic acid,JA)等植物抗病信号传导通路。拟南芥(Arabidopsis thalian)MYB30编码通过调控超长链(very-long-chain)脂肪酸的合成应答病原入侵[6]。MYB44经由WRKY70激活SA介导的防卫反应,抑制JA介导的防卫反应,通过拮抗调节方式调控拟南芥对生物胁迫应答[7]。水稻OsLTR1编码MYB转录因子调控JA防御反应[8]。根据蛋白含有结构域的数量,MYB转录因子分为4种类型,其中R2R3-MYB转录因子参与植物响应生物和非生物胁迫等过程[9]。目前发现的植物MYB在非生物胁迫表达过程主要受miR159、miR828、miR172和miR319等家族的miRNA调控。例如拟南芥ABA刺激促进miR159积累,miR159过表达则抑制MYB101和MYB33转录[10]。
对落叶松-杨栅锈菌(Melampsora larici-populina)E4生理小种侵染欧美杨(Populus × euramericana)研究过程中[11],我们发现欧美杨抗病相关基因的表达并未发生预想的显著上调。以NBS-LRR基因为例,E4生理小种侵染后仅8个TIR-NBS-LRR表达上调,另有11个TIR-NBS-LRR和3个CC-NBS-LRR基因表达下调,其余21个NBS-LRR基因在E4生理小种侵染后表达量未发生显著变化。但,与抗病相关的NAC、WRKY和MYB等转录因子基因表达量却发生显著变化。大量研究表明miRNA参与植物生长发育和胁迫应答中的各个方面,可以在不同层面对靶基因进行调控,是基因表达精细调控必不可少的重要手段,处于复杂调控网络中的关键位置。关于木本植物miRNA在病原菌胁迫中的调控机制的研究相对较少,特别是“杨树-锈菌”体系的miRNA调控机制研究仍处于探索阶段[11, 12]。为揭示欧美杨对E4锈菌感病的分子调控机理,本研究通过miRNA组、降解组(degradome)和基因表达谱(digital gene expression profiling,DGE)等高通量测序技术对锈菌侵染前后欧美杨R2R3-MYB基因及其调控miRNA进行研究。
HTML
-
锈菌接种组(Rust+):E4强致病性落叶松-杨栅锈菌(东北林业大学森林病理学标本室保存)孢子悬浮液(ddH2O,含0.004% Tween 20)接种欧美杨叶间隔期指数(leaf plastochrony index,LPI)为5~9的完全展开的叶片;对照组(Rust-):ddH2O(含0.004% Tween 20)处理欧美杨叶片[13],分别进行3个生物重复。接种量控制在0.01 mL·cm-2 孢子悬浮液。孢子悬浮液对水琼脂培养基喷雾,显微镜下计数,计算接种密度ρ=60个孢子·cm-2。Rust+和Rust-叶片同置于16℃,相对湿度60%,16 h光照·日-1(80 uEm-2 s-1)培养。分别在时间点2 hpi(hours post inoculation)、6 hpi、12 hpi、24 hpi、48 hpi、96 hpi及168 hpi分别收集Rust+和Rust-叶片等量混合CTAB法提取各自处理组总RNA。
-
根据Illumina Small RNA制备试剂盒说明书(Illumina’s TruSeq Small RNA Sample Preparation Guide 1)构建Rust+和Rust- miRNA组。构建Rust+ 降解组cDNA文库。根据Illumina/Solexa标准步骤(directional mRNASeq sample preparation part #15018460 Rev. A, October 2010. Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA)构建Rust+和Rust- DGE文库。构建好的miRNA组、降解组cDNA文库和DGE文库送联川生物(LC Bio: http://www.lc-bio.com/)进行测序并应用llumina’s Sequencing Control Studio software version 2.8(SCS v2.8)、Illumina’s Real-Time Analysis version 1.8.70 (RTA v1.8.70)、Illumina’s Pipeline version 1.5和ACGT101-miR version 4.2(LC Sciences, Houston, TX, USA)等完成数据均一化[14]和基础数据处理。
-
筛选毛果杨(P. trichocarpa)和拟南芥基因组中的R2R3-MYBs,构建本地数据库,以DGE测序结果结合本实验室欧美杨转录组数据进行BLASTP比对(E值< 1e-10)筛选欧美杨R2R3-MYBs。根据DGE测序结果确定锈菌接种前后R2R3-MYBs表达量变化,log2(rust+/rust-)≥1定义为表达量上调、log2(rust+/rust-)≤-1定义为表达量下调、-1 < log2(rust+/rust-) < 1定义为表达量未发生显著变化。根据伪发现率(false discovery rate,FDR)控制差异表达基因[14]。根据miRNA组和降解组鉴定miRNA与其靶向R2R3-MYBs的调控关系。根据R2R3-MYBs结合域(binding motifs)筛选毛果杨基因组潜在的靶基因,并依据STRING(http://string-db.org/)收录的拟南芥同源基因预测R2R3-MYBs与靶基因的互做关系。对靶基因进行GO(gene ontology)富集分析(http://geneontology.org/)。
-
分别以7个时间点Rust+和Rust-第一链cDNA为模板,应用GoTaq 2-Step RT-qPCR System试剂盒在Bio-Rad iCycler iQTM5荧光定量PCR仪上进行扩增。根据测序结果合成PC-3p-2521022_1引物(mi-F:5′-GTG TCG TGC GGC ACT GAA-3′,mi-R:5′-GAT AAT TGG GCT CCG T-3′)和PndMYB173引物(MYB173-F:5′-GAA GAC GAG GCG TTA CAG AG-3′,MYB173-R:5′-GGC CCT GAT GAT TGT GTC AT-3′)。选用毛果杨18sRNA基因(18S-F:5′-CGA AGA CGA TCA GAT ACC GTC CTA-3′,18S-R:5′-TTT CTC ATA AGG TGC TGG CGG AGT-3′)作为内参基因(positive internal control)[15-16]。使用2步法PCR进行40个循环并测定融解曲线。相对定量法计算3次重复试验初始模板量log2(rust+/rust-)比值,两配对样本t检验差各时间点间异显著性。
1.1. 试验材料与锈菌接种
1.2. 组构建及测序
1.3. 生物信息学分析
1.4. 荧光定量PCR
-
欧美杨被E4强致病性锈菌侵染至7 dpi时叶组织坏死,无过敏反应(hypersensitive response,HR)症状产生,且已产生大量夏孢子堆(图 1 Rust+),ddH2O对照处理组无明显变化(图 1 Rust-)。Rust+组叶片在2 hpi~1 dpi未表现明显症状,2 dpi叶片局部出现细小褪绿斑点,4 dpi叶片可见明显黄色斑点,7 dpi病斑面积扩大,锈菌完成一个生长周期开始形成夏孢子堆。发病过程中未见HR和细胞程序化死亡(programmed cell death,PCD)等抗性症状出现,表明欧美杨为高感病树种,与E4强致病性锈菌构成亲和型互做关系。
-
DGE测序共鉴定到欧美杨230个R2R3-MYB基因,其中log2(rust+/rust-)表达量有差异的基因55个(36个锈菌接种后表达量上调,19个表达量下调),175个表达量未发生显著变化。与毛果杨基因组相比较,有36个毛果杨R2R3-MYBs未在DGE测序中找到同源基因。此外,DGE测序检测到208个MYB相关基因(myb-like gene),其中21个表达量下调、3个表达量下调、其余表达量未发生显著变化。进一步分析表达发生变化的R2R3-MYB基因,有10个锈菌侵染前不表达的R2R3-MYBs在锈菌侵染后表达,另有9个锈菌侵染前表达的R2R3-MYBs在锈菌侵染后停止表达(图 2)。表明,锈菌侵染不但可以调控R2R3-MYBs的表达量,还可以启动或关闭R2R3-MYBs的表达。
-
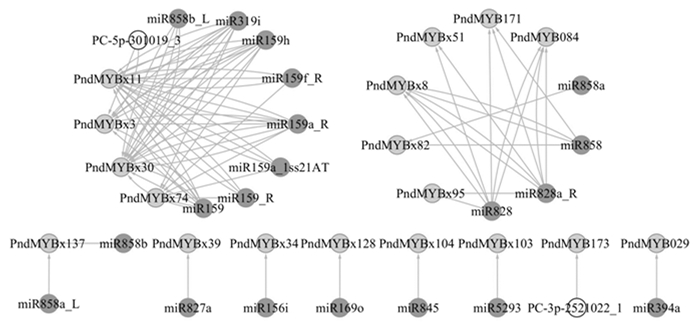
综合分析miRNA组和降解组数据,鉴定到18个R2R3-MYBs与22个miRNA共组成86对转录后调控关系(图 3)。仅有7对转录后调控是单一miRNA对单一R2R3-MYB,其余均为1个miRNA调控多个R2R3-MYBs且每个R2R3-MYB受2个以上(包括2个)miRNA调控。调控miRNA主要集中在miR159(6个)和miR858(5个)2个家族,同时检测到PC-3p-2521022_1和PC-5p-301019_3(图 3黄色标识)2条新miRNA。
-
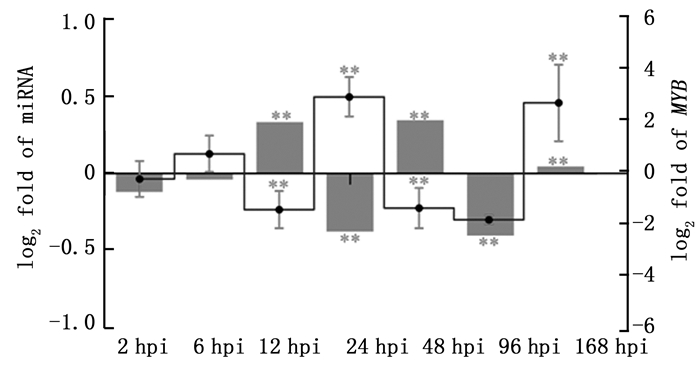
鉴于鉴定到的miRNA与R2R3-MYB转录后调控关系比较复杂,本研究暂选择一对一调控关系的新miRNA调控关系进行荧光定量PCR验证。PC-3p-2521022_1在锈菌接种后7个时间点(2 hpi、6 hpi、12 hpi、24 hpi、48 hpi、96 hpi和168 hpi)表达量变化处于-0.5~0.5之间,变化幅度较小,在12~96 hpi出现往复式波动(图 4柱状图)。PndMYB173表达量变化处于-2~3之间,变化幅度较大,在12~96 hpi同样出现往复式波动,且与其调控miRNA PC-3p-2521022_1呈负调控关系(图 4折线图)。两配对样本t检验结果表明有PC-3p-2521022_1表达量有5个相邻时间点差异极显著(n=3),PndMYB173表达量有4个相邻时间点差异极显著(n=3)。
-
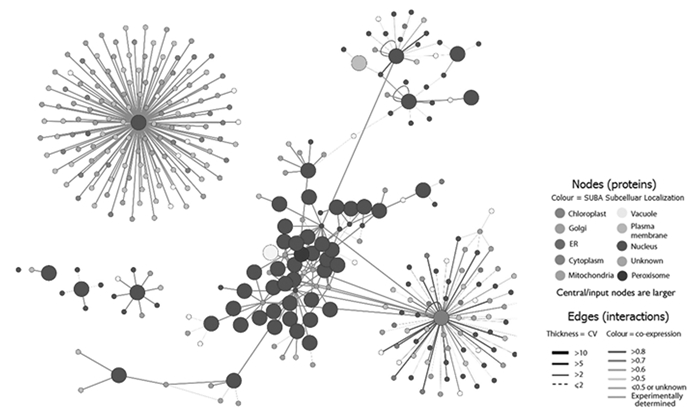
根据结合域,55个差异表达R2R3-MYBs中的48个成功预测到共计336个靶基因。依据STRING数据库预测48个差异表达R2R3-MYBs与靶基因构成400个互做关系(图 5)。其中PndMYBx30具有最多的139个靶基因,构成139个互做关系。根据亚细胞定位,这些靶基因主要定位于细胞核(nucleus)、质膜(plasma membrane)、高尔基体(golgi)、液泡(vacuole)和叶绿体(chloroplast)等细胞器。GO富集分析表明139个靶基因涉及多个与免疫、植物激素相应和抗逆相关的生物过程(biological process,表 1)。
序号
No.GO术语
GO annotation功能描述
Description基因数
Gen numberp值
p value伪发现率
FDR1 GO: 0045087 先天免疫应答innate immune response 5 0.00035 0.0021 2 GO: 0002376 免疫系统进程immune system process 5 0.00046 0.0027 3 GO: 0006955 免疫应答immune response 5 0.00046 0.0027 4 GO: 0050896 响应刺激response to stimulus 34 1.40E-16 1.40E-15 5 GO: 0042221 响应化学刺激response to chemical stimulus 31 6.40E-22 7.90E-21 6 GO: 0010033 响应有机物response to organic substance 29 8.80E-25 1.20E-23 7 GO: 0009719 响应内源性刺激response to endogenous stimulus 28 4.30E-26 6.70E-25 8 GO: 0009725 响应激素刺激response to hormone stimulus 26 3.20E-24 4.30E-23 9 GO: 0005634 细胞核nucleus 21 1.50E-09 3.80E-08 10 GO: 0009751 响应水杨酸刺激response to salicylic acid stimulus 19 1.40E-27 2.20E-26 11 GO: 0006950 应激响应response to stress 19 7.90E-09 6.90E-08 12 GO: 0009753 响应茉莉酸刺激response to jasmonic acid stimulus 18 3.20E-25 4.60E-24 13 GO: 0009737 响应脱落酸刺激response to abscisic acid stimulus 18 4.90E-21 5.90E-20 14 GO: 0009628 响应非生物刺激response to abiotic stimulus 17 3.70E-10 3.30E-09 15 GO: 0006970 响应渗透压刺激response to osmotic stress 15 5.20E-16 4.80E-15 16 GO: 0009739 响应赤霉素刺激response to gibberellin stimulus 14 5.10E-20 5.70E-19 17 GO: 0009723 响应乙烯刺激response to ethylene stimulus 14 9.90E-19 1.10E-17 18 GO: 0010035 响应无机物response to inorganic substance 14 8.80E-17 8.90E-16 19 GO: 0009733 响应生长素刺激response to auxin stimulus 13 7.00E-14 6.30E-13 Table 1. GO enrichment analysis of target genes
2.1. 锈菌接种及症状观察
2.2. 欧美杨R2R3-MYB基因表达量差异
2.3. 欧美杨R2R3-MYBs调控miRNA鉴定
2.4. 欧美杨R2R3-MYB及其调控miRNA表达量验证
2.5. 欧美杨差异表达R2R3-MYBs靶基因预测
-
由miRNA介导的植物抗病性已有比较深入的研究[17-19]。但miRNA转录后调控相关的植物感病性研究还处于起步阶段。以往研究表明效应因子诱导的感病性(effector-triggered susceptibility,ETS)决定杨树对锈菌的互作亲和关系(抗/感病性)。病原侵染后,植物基础抗病性(basal disease resistance)由病原诱导的免疫反应(pathogen-associated molecular patterns triggered immunity,PTI),ETS和效应因子诱导免疫反应(effector-triggered immunity,ETI)的综合反应过程构成[9]。PTI、ETS和ETI过程涉及到感病性增强因子1(enhanced disease susceptibility 1,EDS1)和非小种专化抗病因子1(non-race-specific disease resistance 1,NDR1)激活TIR-NBS-LRR和CC-NBS-LRR等抗性蛋白(R)完成抗病过程。在EDS1/NDR1到R蛋白的抗病性激活过程中涉及到复杂的信号传导和植物激素调节过程。在NDR1将细胞膜外的病原入侵信号传递到膜内后,一系列的TF即被激活,主要包括NAC、WRKY、AP2和MYB等。继而SA、JA和ET等植物激素相关的抗病路径启动。在这个复杂的寄主病原互作体系中,TF与其调控miRNA是决定寄主与病原亲和性的重要因素,如果抗病信号传导受阻或miRNA调控失活寄主即体现为亲和型症状,如果抗病信号顺利传导则寄主将产生HR和PCD等抗性症状。靶基因预测表明欧美杨差异表达R2R3-MYB可启动SA、JA、ET和脱落酸(abscisic acid)等多个植物激素路径。实际接种试验中欧美杨并未发生HR或PCD等症状,表明欧美杨的抗性信号传导过程可能出现了阻碍。本研究仅对一对R2R3-MYB转录后调控进行了荧光定量PCR验证,这还不足以检验出这种阻碍是否出现在R2R3-MYB转录后调控的层次上。因此,有必要对86对转录后调控关系逐一验证,综合分析欧美杨的感病性机理。
-
E4强致病锈菌侵染导致亲和型树种欧美杨23.9%的R2R3-MYBs表达量发生变化,锈菌侵染不但可以影响R2R3-MYBs的表达量,还可以启动或关闭R2R3-MYBs的表达。欧美杨在E4强致病锈菌胁迫条件下,R2R3-MYBs转录后主要受miR159和miR858家族的miRNA调控。已验证的R2R3-MYB与miRNA存在负向转录后调控关系。R2R3-MYBs靶基因涉及多个与免疫、植物激素相应和抗逆相关的生物过程。











 DownLoad:
DownLoad: