-
由松褐天牛(Monochamus alternatus)传播的松材线虫病(Bursaphelenchus xylophilus)是我国最为严重的病虫害,目前已经传播到我国南方除海南省以外的其它13个省及北方的河南、陕西、山东省和辽宁省,每年致死大量的松树,造成了严重的经济和生态损失[1]。利用天敌昆虫生物防治其传播媒介松褐天牛是持续防控松材线虫病的有效措施之一[1-3]。目前,广泛使用的松褐天牛的天敌主要是肿腿蜂和花绒寄甲(Dastarcus helophoroides Fairmaire) [1-8],其中, 肿腿蜂有管氏肿腿蜂(Sclerodermus guani Xiao et Wu)[5, 9]、川硬皮肿腿蜂(S. sichuanensis Xiao) [7]和松褐天牛肿腿蜂(S. alternatusi Yang)[8]3个种应用到林间防治松褐天牛。在林间,肿腿蜂主要寄生松褐天牛的13龄初低龄幼虫[8],而花绒寄甲主要寄生中老龄幼虫、蛹及少数初羽化尚未出孔的成虫[1, 3]。2013年在贵州遵义,笔者发现了寄生松褐天牛中老龄幼虫的另一种重要天敌——松褐天牛深沟茧蜂(Iphiaulax monochamusi Yang) [10],其在有的林分自然寄生率达30%。该寄生蜂在遵义地区一年2代,世代重叠,是一种良好的可利用于生物防治松褐天牛的寄生蜂新种。1头松褐天牛幼虫上可寄生111头松褐天牛深沟茧蜂,但不管寄生1头深沟茧蜂还是多头,最终均能将松褐天牛幼虫杀死。为了明确这种优良寄生蜂的寄生率与寄主树木、寄主和环境因子的关系,2014年,笔者在贵州省遵义市马尾松林分中,先后解剖了有松褐天牛的马尾松死树46株,调查研究了寄主树木—害虫—天敌三者之间的关系,以期明确这种寄生蜂与寄主松褐天牛之间的关系,为生物防治利用该深沟茧蜂打下基础。
HTML
-
研究样地位于贵州省遵义市遵义县龙坑镇共青湖(27°35′51.87″ N,106°50′21.07″ E),海拔900950 m。研究地属亚热带季风气候区,年均降水量1 200 mm,年均日照1 146.9 h,年均气温14.7℃,无霜期270 d。林分主要为马尾松(Pinus massoniana Lamb.)林,多数区域为纯林,部分区域有枫香(Liquidambar formosana Hance)和老鼠矢(Symplocos stellaris Brand)等阔叶树,阔叶树占比在0%20%之间。马尾松树龄3550 a,树高1025 m,胸径560 cm,密度为6001 200株·hm-2。主要杂灌植物有毛杜鹃(Rhododendron radendum Fang)、六月雪(Serissa japonica (Thunb.) Thunb.)、山苍子(Litsea cubeba (Lour.) Pers.)、油茶(Camellia oleifera Abel)和悬钩子(Rubus corchorifolius Linn.f.)等,杂灌高度100180 cm,林下植被盖度45%100%,枯枝落叶层厚度15 cm。林地内枯死松树数量为36株·hm-2,松褐天牛虫口密度为193头·株-1,属轻中度发生[11]。
-
2014年4—9月,在上述试验林区,选择有松褐天牛的枯死马尾松作为样株。调查其周围林地内(200 m2)的林型(马尾松所占比例)、主林层郁闭度和马尾松株数。详细记载每株样株所在的坡位(山脊、上坡、中坡、下坡和山坳)、坡向(阳坡、阴坡、半阴半阳坡),用坡度测量仪测量坡度、林下植被盖度(灌木和草本层的总盖度)、杂灌高度和枯枝落叶层厚度[11-13]。将被松褐天牛危害致死树木伐倒后测量树高、胸径和树龄,以0.5 m为一段分段解剖,详细记载每段树木韧皮部和木质部的松褐天牛幼虫数量,被松褐天牛深沟茧蜂寄生的数量(以观察到有松褐天牛深沟茧蜂的蛹、幼虫或已羽化的茧壳为准), 并将采集到的松褐天牛深沟茧蜂蛹和幼虫带回室内饲养至成虫,同时将被该茧蜂寄生致死后留存的松褐天牛幼虫头壳带回室内,用带有测微尺的Motic体视显微镜20倍下测量其头壳宽度以确定寄主幼虫龄期[14]。同时, 记载被其它天敌寄生的松褐天牛幼虫数量。根据公式计算:松褐天牛深沟茧蜂寄生率=被松褐天牛深沟茧蜂寄生的天牛幼虫数/(松褐天牛活幼虫数+被松褐天牛深沟茧蜂寄生的天牛幼虫数+被其它天敌寄生的天牛幼虫数)];其他天敌寄生率=被其他天敌寄生天牛幼虫数/(松褐天牛活幼虫数+被松褐天牛深沟茧蜂寄生的天牛幼虫数+被其它天敌寄生的天牛幼虫数)×100%。4月下旬调查1株,5—9月平均每旬调查3株,每月9株,共调查46株马尾松,其中,4—5月调查的10株为2013年枯死的马尾松,6—9月调查的36株为2014年4月中下旬所设诱木。
为便于数据整理,对各环境因子进行编号:林型X1、坡位X2、坡向X3、坡度X4、主林层郁闭度X5、林下植被盖度X6、杂灌高度X7、枯枝落叶层厚度X8、马尾松密度(每公顷株数)X9和其他天敌寄生率X10。
-
对于定性记载的环境因子,采用等级数量化处理,例如坡位,取“山脊”=5,“上坡”=4,“中坡”=3,“下坡”=2,“山坳”=1;坡向,取“阳坡”=3,“半阴半阳坡”=2,“阴坡”=1 [10-12]。本文用公式:$X = \frac{{X_i^a}}{{X_i^{\max }}} $ (i=1,2…13,a=1,2…45)对数据进行无量纲化处理,即每一列的数据除以该列中的最大值。采用SPSS 17.0统计分析软件进行逐步回归分析,用SPSS中的One-Way ANOVA进行方差分析,用Duncan氏新复极差法检验,比较各处理之间的差异水平。
1.1. 研究地概况
1.2. 调查方法
1.3. 数据统计与分析
-
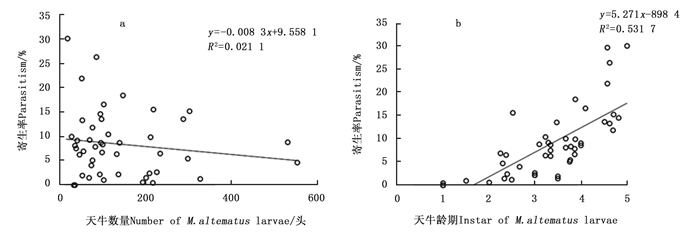
松褐天牛深沟茧蜂的寄生率与松褐天牛幼虫的数量没有明显的关系(图 2a),而与松褐天牛幼虫的龄期呈线性关系(y=5.271x-8.698; F=51.091, df=1, 46, P=0.000 1, R=0.729 2) (图 2b)。表明松褐天牛深沟茧蜂偏好寄生35龄的松褐天牛中老龄幼虫。
-
松褐天牛深沟茧蜂对不同高度分布的松褐天牛的寄生率差异显著(F=4.544, df=4, 124, P=0.000 1)(图 3),其中,松褐天牛深沟茧蜂对位于树干上部的松褐天牛寄生率最高,达27.38%;对位于树干中上部的寄生率次之,为18.23%;对位于树干中部的寄生率为10.50%;对位于树干中下部和下部的天牛寄生率较低,仅为6.13%和1.73%。上部和中上部被寄生的天牛多数在木质部,而中下部和下部被寄生的天牛多数在韧皮部。
-
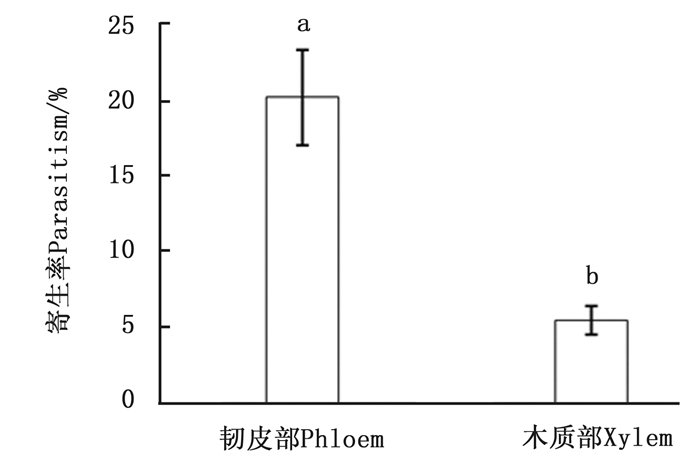
松褐天牛深沟茧蜂对位于马尾松树干韧皮部和木质部的松褐天牛幼虫寄生率差异显著(F=19.601, df=1, 63, P=0.000 1)(图 4)。对位于韧皮部寄主的寄生率最高达57.14%,平均为20.18%;而对位于木质部中的松褐天牛幼虫的寄生率最高为18.68%,平均仅为5.46%。
-
对环境因子与松褐天牛深沟茧蜂寄生率的关系进行了逐步回归分析,结果(表 1)表明:影响松褐天牛深沟茧蜂的关键因子是坡位(X2)和其它天敌寄生率(X10),其中,坡位与松褐天牛深沟茧蜂的寄生率呈正相关,而其它天敌寄生率与松褐天牛深沟茧蜂的寄生率呈负相关。
变量
Variable林型
Crop type X1坡位
Slope position X2坡向
Exposure X3坡度
Slope X4郁闭度
Canopy density X5植被盖度
Percentage of vegetation X6植被高度
Height of vegetation X7枯枝层厚度
Thickness of branch litter X8马尾松密度
Density of Pinus massoniana X9其它天敌寄生率
Parasitism rate of other natural enemies X10偏相关系数Partial correlation coefficient 0.176 7 0.617 4 0.077 0 -0.133 9 -0.126 5 0.306 0 -0.306 0 0.229 8 -0.160 4 -0.467 7 t检验值 1.062 0 4.642 6 0.456 8 0.799 5 0.754 4 1.901 6 1.901 6 1.397 2 0.961 5 3.130 0 P 0.295 3 0.000 1 0.650 5 0.429 2 0.455 5 0.065 2 0.065 2 0.170 9 0.342 7 0.003 5 Table 1. The partial correlation coefficient of each variable and t-test
-
马尾松主干上其它天敌的寄生率与松褐天牛深沟茧蜂的寄生率呈显著的负相关(y=-0.697x+20.088; F=63.672, df=1, 45, P=0.000 1, R=0.769 1) (图 5),即其它天敌寄生率越高,松褐天牛深沟茧蜂的寄生率越低。
-
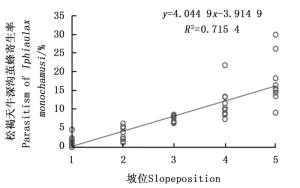
调查发现:寄主树木马尾松林地坡位与松褐天牛深沟茧蜂寄生率呈显著的正相关(y=4.045x-3.915; F=110.622, df=1, 45, P=0.000 1, R=0.845 8) (图 6), 即松褐天牛深沟茧蜂偏向寄生处于山脊和上坡位的马尾松上的松褐天牛。
2.1. 马尾松树高、胸径和树龄对松褐天牛深沟茧蜂寄生率的影响
2.2. 松褐天牛深沟茧蜂寄生率与天牛数量和龄期的关系
2.3. 松褐天牛深沟茧蜂寄生率与寄主在树干上分布位置的关系
2.3.1. 松褐天牛深沟茧蜂对位于不同树干高度的松褐天牛幼虫寄生率的差异
2.3.2. 松褐天牛深沟茧蜂对马尾松韧皮部和木质部的松褐天牛幼虫寄生率的差异
2.4. 松褐天牛深沟茧蜂寄生率与环境因子的关系
2.4.1. 逐步回归分析环境因子与松褐天牛深沟茧蜂寄生率的关系
2.4.2. 马尾松主干上其它天敌的寄生率与松褐天牛深沟茧蜂寄生率的关系
2.4.3. 寄主树木林地坡位与松褐天牛深沟茧蜂寄生率的关系
-
寄主植物—害虫—天敌的三级关系一直是昆虫生态学的热点问题[15],而天敌位于这个系统中的顶级,其在维持害虫种群数量上发挥着重要作用[16]。我国8 000余种林木害虫,目前爆发成灾的仅200余种,绝大多数害虫都因为天敌的存在而种群较低,没有造成严重危害。在这爆发成灾的害虫中,蛀干害虫是对林木危害最严重的一类,其中,松褐天牛、光肩星天牛、云斑天牛、青杨天牛、桑天牛和栗山天牛等为代表的天牛类害虫年发生面积均在百万亩以上[1];而全球气候变暖,天牛幼虫生活隐蔽且生活史重叠,成虫期长,化学防治难度大,天敌作用小被认为是这些天牛类蛀干害虫在我国爆发成灾的主因[15]。另外,化学药剂的使用在消灭部分害虫的同时亦将天敌一同消灭,造成植物—害虫—天敌之间难以建立平衡的生态系统,从而导致害虫的再爆发或次要害虫的爆发;而利用天敌开展天牛类蛀干害虫的生物防治,是以维护生态系统平衡的角度为出发点,以实现植物—害虫—天敌的种群平衡,从而实现对蛀干害虫的有效和持续控制。
松褐天牛因携带松材线虫传播松材线虫病而成为防治松材线虫病的关键。在松材线虫病疫区,人们往往不允许有松褐天牛的存在,即使是较低的数量仍然存在传播松材线虫病的风险。因此,即使是在诸如安徽九华山释放花绒寄甲,其寄生率达90%以上的松褐天牛[3],仍然不能消除人们对生物防治松褐天牛控制松材线虫病的疑虑。在防控松材线虫病上,人们更愿意相信传统的疫木处理方式(皆伐后火烧或者粉碎造纸),而这些方法在致力于将松褐天牛消灭干净的同时将松褐天牛的天敌也一并消灭了。
事实上,松褐天牛在我国的天敌资源很丰富,目前报道的松褐天牛天敌已有100余种,其中,天敌昆虫50余种,病原微生物17种,捕食性鸟类33种[1, 17-18];但仍然有新的天敌被发现,2008年发现于云南的寄生松褐天牛的松褐天牛肿腿蜂,该肿腿蜂不仅个体大,雌蜂有翅率高,十分有利于防治松褐天牛,经分子生物学研究,该肿腿蜂在28S等基因上与我国已报道的管氏肿腿蜂和川硬皮肿腿蜂等明显不同,表明其极有可能为一新种[19];而2011年在安徽九华山发现了寄生松褐天牛卵的金小蜂,为一新种,为国内外首次报道[17]。近几年,笔者在贵州遵义进行调查过程中,亦发现了2种寄生松褐天牛低龄幼虫的寄生蜂和寄生中老龄幼虫的松褐天牛深沟茧蜂[14]。这些天敌在控制松褐天牛种群上作用明显,如松褐天牛深沟茧蜂,在部分马尾松上自然寄生率达30%,再加上其它天敌的作用,马尾松上能成功羽化出成虫的松褐天牛数量并不多,但在松材线虫病疫区,即使是极少量的松褐天牛存在,也仍然有传播松材线虫病的风险。
因此,探讨如何安全处理疫木,同时又保护好天敌成为新的课题。从2009年起,笔者在安徽九华山和贵州遵义尝试利用铁丝网罩网处理疫木,同时释放天敌昆虫,建立林间天敌繁育场,同时让其他天敌昆虫能够从铁丝网钻出,而松褐天牛不能钻出,取得了良好的控制松褐天牛种群数量的效果[20]。这与传统的疫木处理方式相比,有明显的优点,一是多数疫木可以就地处理,不用搬下山,节省人力物力;二是有效保护了松褐天牛的天敌;三是利用死树中的松褐天牛幼虫建立了林间天敌自然繁育场,增加了林间天敌数量,从而对林间残留的松褐天牛起到持续的控制作用。对于松材线虫病疫区而言,通过23年的持续努力,就可以将松褐天牛的种群降低到很低的水平,从而控制松材线虫病的蔓延扩散[14, 20]。在上述2个试验区,松材线虫病致死松树已全面下降[1, 14, 20-21]。2013年起,江西省吉水县林业局采用购买社会化防治服务,在疫区全面推广应用该项技术,约700 hm2的林地,经过1年的综合治理,死树由治理前的15 000余株下降到不足1 000株,成效显著。该项技术易于掌握,只要操作到位,有效控制松材线虫病已不再是难题。虽然在短期内需要投入较大的人力物力,但长远来看,还是成本比较低的。可以预见的是,该项技术必将在松材线虫病的治理中发挥关键作用。










 DownLoad:
DownLoad: