-
马尾松(Pinus massoniana Lamb.)是我国南方重要荒山造林树种,具有耐贫瘠,速生丰产等优点,被誉为“先锋树种”。松材线虫病被视为松树的“癌症”,其具有危害大、隐蔽性强、致使寄主快速死亡并可人为远距离传播等特点,致使防治该病害的工作存在较大困难,松材线虫病疫点数量和发生面积逐年增大。有鉴于此,明确马尾松抗松材线虫病的基因表达调控过程是当前利用现代生物学技术防控松材线虫病害研究中不可缺少的部分。
非编码微小RNA (microRNA, miRNA)由于具有高效沉默靶向mRNA表达的特性,成为当前生命科学研究中最受关注的对象之一[1-2]。这种长度为20~24 nt的单链非编码小RNA能够以RNA诱导沉默复合体的形式结合到靶基因上,对靶基因进行降解或抑制靶基因的翻译,从而在基因转录后对其进行表达沉默,降低基因的表达丰度。这一新奇的基因表达调控方式自从21世纪初发现以来已受到国内外研究团队的密切关注[3-5]。
近年来的诸多研究均表明,miRNA在调控植物生长发育和响应逆境胁迫的过程中起着十分重要的作用,这包括调控植物抗旱、耐冷、抗病等多种行为[6-11]。在林木研究中,Wan等[12]利用本地BLAST和MIREAP程序从高山松(Pinus densata Mast.)的转录组数据中鉴定得到了34个保守的miRNA,其中,25个miRNA家族共有72个靶基因,且大部分miRNA与mRNA具有靶向作用关系。Quinn等[13]在火炬松(Pinus taeda L.)的序列表达标签中发现12个未被报道的miRNA,这些miRNA作用的靶基因参与表达调控、代谢和信号转导。此外,Lu等[14]在对火炬松miRNA及其与松梭锈病病害发生的相关性研究中,从火炬松茎干的木质部克隆并鉴定了26个miRNA,其中,9个家族miRNA能够有效调控43个靶基因的表达。Xie等[15]测定了松材线虫侵染1、2、3 d及未受侵染的对照马尾松样本中miRNA表达谱,结果显示,侵染不同天数下的马尾松针叶中有10个miRNA均较对照样本发生差异表达,其对应的靶基因在植物激素信号通路等途径富集。与此同时,笔者前期也测定了松材线虫侵染1、2、3 d的马尾松针叶mRNA表达谱。本文在上述研究的基础上,进一步研究松材线虫侵染下,马尾松针叶的mRNA及miRNA表达关联情况,通过比较二者的表达变化模式,明确miRNA对重要mRNA的有效调控作用,为揭示马尾松响应松材线虫侵染胁迫下的转录调控过程提供参考。
HTML
-
以前期通过RNA-seq测序获得松材线虫(Bursaphelenchus. xylophilus)侵染1、2、3 d下的2年生马尾松及其对照样本针叶中miRNA和mRNA表达谱文库为研究对象[15]。处理及对照马尾松针叶mRNA和miRNA由广州基迪奥生物科技有限公司采用Illumina HiSeqTM2 500进行测序,其中,mRNA测序采用PE125 (paired end 125 bp)策略,miRNA测序采用SE50 (single end 50 bp)策略。
-
使用STEM (Short Time-series Expression Miner, http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~jernst/stem)软件分别绘制松材线虫侵染1、2、3 d下的马尾松及其对照样本针叶的miRNA和mRNA不同表达变化模式图。
-
挑选具有靶向关系的差异表达mRNA和差异表达miRNA,运用斯皮尔曼等级相关法计算这些miRNA-mRNA对在各自对应的两组模式中的相关性,得到相关系数。由于miRNA对其靶向mRNA具有负调控作用,因此,将斯皮尔曼等级相关系数小于等于-0.5的miRNA-mRNA对列出,得到目标miRNA及其靶向负调控的mRNA。
-
分别提取关联表达的miRNA与mRNA在松材线虫侵染1、2、3 d下的马尾松及其对照样本针叶中的表达量,采用广州基迪奥生物科技有限公司的OmicShare在线软件平台(http://www.omicshare.com/),绘制松材线虫侵染1、2、3 d的马尾松较对照马尾松样本针叶中发生关联表达的miRNA与mRNA表达量热图。
1.1. 供试材料
1.2. 研究方法
1.2.1. 松材线虫侵染下马尾松针叶的差异表达mRNA及miRNA的表达模式
1.2.2. miRNA与mRNA的表达关联分析
1.2.3. 表达量关联的miRNA及mRNA的热图
-
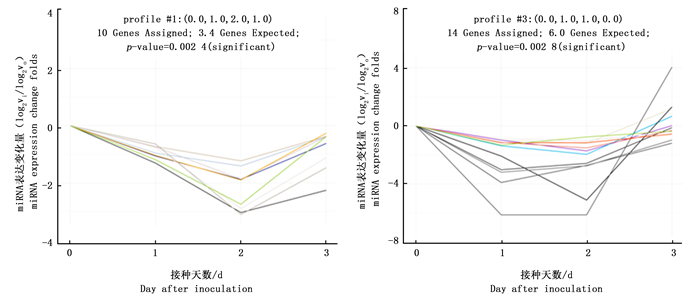
基于前期RNA-seq得到的松材线虫侵染1、2、3 d的马尾松及其对照样本针叶的miRNA表达谱数据,分析不同miRNA的表达变化模式,结果显示:侵染不同天数的马尾松针叶的miRNA表达量变化呈多种模式(profile),其中profile 1和3中的miRNA在侵染不同天数下的马尾松中较对照组表达变化差异显著,其p值均小于0.05,且这些miRNA在侵染第2天的马尾松针叶中的表达较对照样本变化程度最大,说明松材线虫侵染2 d的马尾松针叶中基因表达响应强烈。通过对各组不同表达变化模式的miRNA数量进行统计,结果显示:profile 1和3中分别有10个和14个miRNA (图 1)。
-
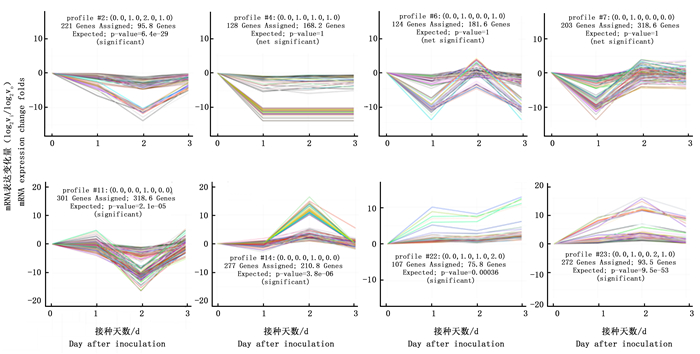
进一步研究了RNA-seq得到的松材线虫侵染1、2、3 d的马尾松及其对照样本针叶的mRNA表达谱,对mRNA的表达变化模式进行分析,结果显示mRNA表达变化模式具有显著性的有8组,分别是profile 2 (119个基因),profile 4 (205个基因),profile 6 (321个基因),profile 7 (376个基因),profile 11 (374个基因),profile 14 (282个基因),profile 22 (88个基因)和profile 23 (123个基因) (图 2)。
-
为研究松材线虫侵染的马尾松针叶中可能由miRNA的降解作用而引起表达变化的mRNA,进一步对表达变化模式相反的miRNA和mRNA进行关联性分析。结果在miRNA表达变化模式中获得15个具有统计学关联性的miRNA(表 1),与这些miRNA表达变化模式相反的靶标mRNA为12个,这些基因包括: (1)与病原识别相关的类CC-NBS-LRR抗性基因(CC-NBS-LRR resistance-like gene)、NBS、TIR/NBS以及ACRE (Avr9/Cf-9rapidly elicited defense-related gene, ACRE); (2)与转录调控相关的类MYB转录因子MBF1 (MYB-like transcriptional factor, MBF1); (3)与防御相关的,位于保守激酶2和P-Loop结构阈区间的抗性基因(resistance gene, region between conserved kinase-2 and P-Loop domains)、棉子糖合成酶家族蛋白质异构体1 (Raffinose synthase family protein isoform 1)基因、类乙烯不敏感蛋白3异构体1(ethylene insensitive 3-like isoform 1)基因; (4)与植物生长发育相关的,类copia反转录转座子(copia-like retrotransposable element)、1, 2-α-L-岩藻糖苷酶(1, 2-alpha-L-fucosidases)、5’-腺苷酰硫酸还原酶3(5’-adenylylsulfate reductase 3)、反转录酶(reverse transcriptase)等的编码基因。在这些表达关联的miRNA与mRNA中,novel-m0040-3p和novel-m0040-5p靶向作用的CC-NBS-LRR抗性基因,miR946、novel-m0136-3p、novel-m0051-3p靶向作用的ACRE基因,二者均是植物识别病原信号的直接基因。
miRNA 表达量(TPM)
miRNA expression预测勒标mRNA
Predicted target mRNAmRNA表达量
(RPKM) mRNA expressionmiRNACT TR1 TR2 TR3 CT TR1 TR2 TR3 病原识别功能(pathogen recognition) miR946 7 792.11 9 754.86 8 739.33 9 491.99 R gene, a homology of Avr9/Cf-9 rapidly elicited defense-related gene (ACRE) (Pinus sylvestris) 316.78 137.35 159.70 221.38 novel-m0136-3p 449.23 509.23 520.53 539.26 R gene, a homology of Avr9/Cf-9 rapidly elicited defense-related gene (ACRE) (Pinus sylvestris) 316.77 137.35 159.69 221.38 novel-m0051-3p 393.08 509.23 453.00 504.99 R gene, a homology of Avr9/Cf-9 rapidly elicited defense-related gene (ACRE) (Pinus sylvestris) 316.77 137.35 159.69 221.38 novel-m0040-5p 122.84 289.90 194.14 172.64 CC-NBS-LRR resistance-like gene(Pinus lambertiana) 2.27 0 0 0 novel-m0040-3p 66.68 153.60 136.93 78.24 CC-NBS-LRR resistance-like gene(Pinus lambertiana) 2.27 0 0 0 miR472 5.62 0.69 0.94 5.17 NBS (Pinus taeda) 3.67 5.31 8.40 2.54 miR3705 6.32 0.69 5.63 2.59 TIR/NBS (Pinus taeda) 0.53 1.33 0.50 3.68 转录调控功肯旨(transcriptional regulation) miR858 197.94 100.32 60.03 200.44 MYB-like transcriptional factor MBF1 (Picea mariana) 0.94 3.33 1.85 1.14 防御功能(defense) miR156 1 000.25 2 315.04 1 365.58 1 379.83 Raffinose synthase family protein isoform 1 (Theobroma cacao) 8.83 4.15 13.79 3.98 miR5658 4.91 1.38 1.88 0.01 resistance gene;region between conserved kinase-2 and P-Loop domains (Pinus radiate) 0.24 1.55 0.46 2.96 novel-m0012-5p 4.83 0.01 0.01 0.01 ethylene insensitive 3-like isoform 1 (Cucumis sativus) 5.47 6.57 6.20 6.43 植物生长发育相关(plant growth and development) novel-m0172-3p 155.13 69.19 69.40 105.39 copia-like retrotransposable element (Arabidopsis thaliana) 1.04 2.12 1.09 1.78 novel-m0071-5p 80.72 36.67 28.13 65.31 1, 2-alpha-L-fucosidases (Theobroma cacao) 2.11 3.10 2.38 0.95 novel-m0157-3p 25.27 13.15 51.58 33.62 5’adenylylsulfate reductase 3, chloroplastic-like isoform 1 (Vitis vinifera) 5.09 10.05 1.88 3.64 novel-m0019-3p 124.94 56.04 87.22 128.03 reverse transcriptase (Arabidopsis thaliana) 1.42 2.80 1.84 0.25 注:CT:对照; TR1:侵染1天; TR2:侵染2天; TR3:侵染3天。
Note:CT:Control;TR1:1 d after infestation;TR2:2 d after infestation;TR3:3 d after infestation.Table 1. The correlation between miRNA and mRNA expression pattern on needle leaf of P.massoniana after different days of B.xylophilus infestation comparison with the control group
深入分析表达关联的miRNA与mRNA的基因信息可见,松材线虫侵染后,马尾松针叶中的类CC-NBS-LRR基因、ACRE基因受到其对应miRNA的沉默作用后,其在受侵染的马尾松样本中的表达都较对照样本中的表达量低,而相应的miRNA则在受侵染样本中的表达量均高于对照样本,miRNA与靶基因的表达变化模式相反体现了miRNA对靶标mRNA的负调控作用。此外,位于保守激酶2和P-Loop结构域之间的类似抗性基因与miRNA5658关联,其中,miRNA5658在处理样本中下调表达,而其对应的靶标基因即抗性基因则上调表达。逆转录酶基因在侵染1、2天的样本中上调表达并在第3天较对照样本表达下调,其相应的novel-m0019-3p则在侵染第1、2天的处理样本中下调表达,而在第3天表达上调。与光合作用相关的5’-腺苷酰硫酸还原酶-3的编码基因在处理的第1天表达上调,在随后的第2、3天表达下调,对应的novel-m0157-3p则是先下调表达后上调表达,符合其对靶标mRNA的调控特征。此外,编码棉子糖合成酶家族蛋白质异构体1的基因在侵染第1天的样本中的表达较对照样本下调,侵染第2天的处理样本中的表达则高于对照样本,侵染第3天的表达又低于对照样本,其相应的miRNA156则在处理第1天的样本中表达量显著增加,随后在侵染第2、3天时表达量降低(图 3)。
2.1. 松材线虫侵染下马尾松针叶的miRNA表达模式分析
2.2. 松材线虫侵染下马尾松针叶的mRNA表达模式分析
2.3. 松材线虫侵染下,马尾松针叶中miRNA与mRNA的关联统计
-
就林木遗传育种而言,由于传统技术存在周期长、成本高、遗传体系建立难度大等缺点,致使优良林木品种的育种效率受到较大限制,严重影响了优良品种的推广应用和林业产业的健康发展。近年来,随着现代分子生物学研究技术的不断发展及在其它作物育种领域的成功应用,未来利用分子遗传技术培育优良品种也将成为现代林木育种的新趋势与新方向[16],其中,发掘林木抗逆防御的相关基因是实现其分子遗传育种的重要基础和努力方向[17-18]。通过比较同一种林木在环境条件变化下的转录组表达变化情况,能够明确供体样本的基因表达调控过程,并获得目标基因。笔者前期利用RNA-seq研究发现,松材线虫侵染抑制了马尾松针叶中R基因、类CC-NBS-LRR基因等与抗病能力密切相关的基因的表达,其中,R基因与樟子松(Pinus sylvestris)的PsACRE (a homology of Avr9/Cf-9 rapidly elicited defense-related gene)的相似度为99%,而PsACRE属于富含亮氨酸重复(LRR)家族的基因,其在接种担子菌的樟子松中表达增强[19]。课题组进一步克隆了马尾松ACRE基因的全长CDS,并成功遗传转化拟南芥[20],对转基因拟南芥及其未转基因的野生型植株接种松材线虫,比较2种拟南芥的抗性能力,结果显示:转基因拟南芥对松材线虫的抵抗更强,从而证实了ACRE基因对松材线虫抗病能力的调控作用,也表明该基因可作为分子培育抗病马尾松的重要候选基因。深入揭示这些抗病密切相关基因的表达调控行为,有利于阐明马尾松抗病能力的内在机制。
转录组层面的基因表达变化包括mRNA和小RNA等的表达水平变化,其中,小RNA是一类短的调控RNA,其不具有编码基因的功能,但其通过互补序列沉默基因,在细胞的基因表达调控过程中具有重要的作用。这些小的寡核苷酸片段通过与沉默复合体(RISC)结合并作用于靶标mRNA,降解靶标mRNA而影响基因表达[21],其中,由于miRNA在进化过程中十分保守,且大部分植物的miRNA只在特定组织和特定阶段表达[22],因此,miRNA是当前植物表观遗传学研究的一个热门方向。本文结合前期研究结果发现,松材线虫侵染的马尾松针叶中miRNA的表达丰度随着侵染时间延长也在发生改变,其中大部分miRNA在侵染第2天的马尾松针叶中表达变化最强烈[15],这预示该时期下的马尾松针叶中的mRNA表达将受到miRNA的有力调控,并可从中发掘调控马尾松抗松材线虫病害能力的相关miRNA和mRNA,为抗病马尾松的分子育种提供基因资源。
对miRNA和mRNA的表达关联分析显示,马尾松针叶中类CC-NBS-LRR抗性基因、属于LRR家族的ACRE基因等的表达分别受到了miR946,novel-m0136-3p和novel-m0051-3p,以及novel-m0040-5p和novel-m0040-3p的调控。CC-NBS-LRR类抗病相关基因是调节植物抗病免疫反应的一类重要基因,NBS (nucleotide binding site)存在于真核生物的许多蛋白中,主要负责ATP的水解以及释放信号,其N端包含一个TIR (Toll and interleukin-1 receptor)结构[23]。CC-NBS的增强表达可以激活植物的抗病防御能力;与之相似的还有一个编码类似抗性基因的片段(similar to resistance gene; region between conserved kinase-2 and P-Loop domains),该片段介于保守激酶2(conserved kinase-2)和P-Loop结构域(P-Loop domains)之间,可能受到miR5658的调控。由此可见,马尾松中抗病密切相关的CC-NBS-LRR, LRR等基因的表达均受到了相应的miRNA的调控。在此基础上,通过外源调控技术抑制负调控作用的miRNA表达,以及转基因技术提高抗病基因在马尾松中的表达均有望获得抗病能力提高的马尾松株系,促进抗病马尾松的培养。
miRNA还调控转录因子的表达,如miR585调控的MYB-like transcriptional factor MBF1,这是一类含有MYB结构域的转录因子,这种结构域具有一段约51~52个氨基酸的肽段,包含一系列高度保守的氨基酸残基和间隔序列,参与植物苯丙烷类次生代谢途径的调节[24],苯丙烷类代谢是植物主要的3条次生代谢途径之一,它起始于苯丙氨酸,经过几个共同步骤后,分成2个主要分支途径,其中一条分支称为黄酮类代谢途径,这些次生物质参与植物的防御反应,属于植保素类物质。可见松材线虫侵染马尾松可能影响了其植保素类物质合成的上游调控基因,进而改变这些物质的合成能力。除此之外,马尾松针叶中与叶绿体内硫酸盐吸收与还原相关的5’-腺苷酰硫酸还原酶,与遗传信息传递相关的反转录酶基因,与植物生长发育及防御相关的1, 2-α-L岩藻糖苷酶(1, 2-alpha-L-fucosidases)、棉子糖合成酶等基因的表达也受到了相应miRNA的调控,这些基因分别参与植物体生长发育、遗传信息传递以及抗逆境胁迫的过程[25-27],其表达丰度的变化将最终影响马尾松针叶细胞的代谢能力。上述基因及调控其表达的miRNA的发掘也为马尾松的分子育种提供了基因基础。
-
本文通过对松材线虫侵染下,马尾松针叶miRNA和mRNA的表达变化模式及其关联情况进行研究,结果推测miRNA负调控了松材线虫侵染下的马尾松针叶中相关防御、代谢及转录调控基因的表达,且CC-NBS-LRR、ACRE等抗病密切相关基因的表达也可能受到相应miRNA的负调控。进一步采用miRNA和靶标mRNA的共表达能够验证miRNA对靶标miRNA表达的有效负调控作用。马尾松响应松材线虫侵染的抗性基因及调控其表达的小RNA的发掘可为抗病马尾松的分子设计与遗传育种提供重要的理论基础与基因资源,并为松类树木的抗病机制研究提供借鉴,以此加快抗病松树的现代分子育种进程。






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: